Publications
Highlights
At the end of this page, you can find the full list of publications. All papers are also available on GoogleScholar.
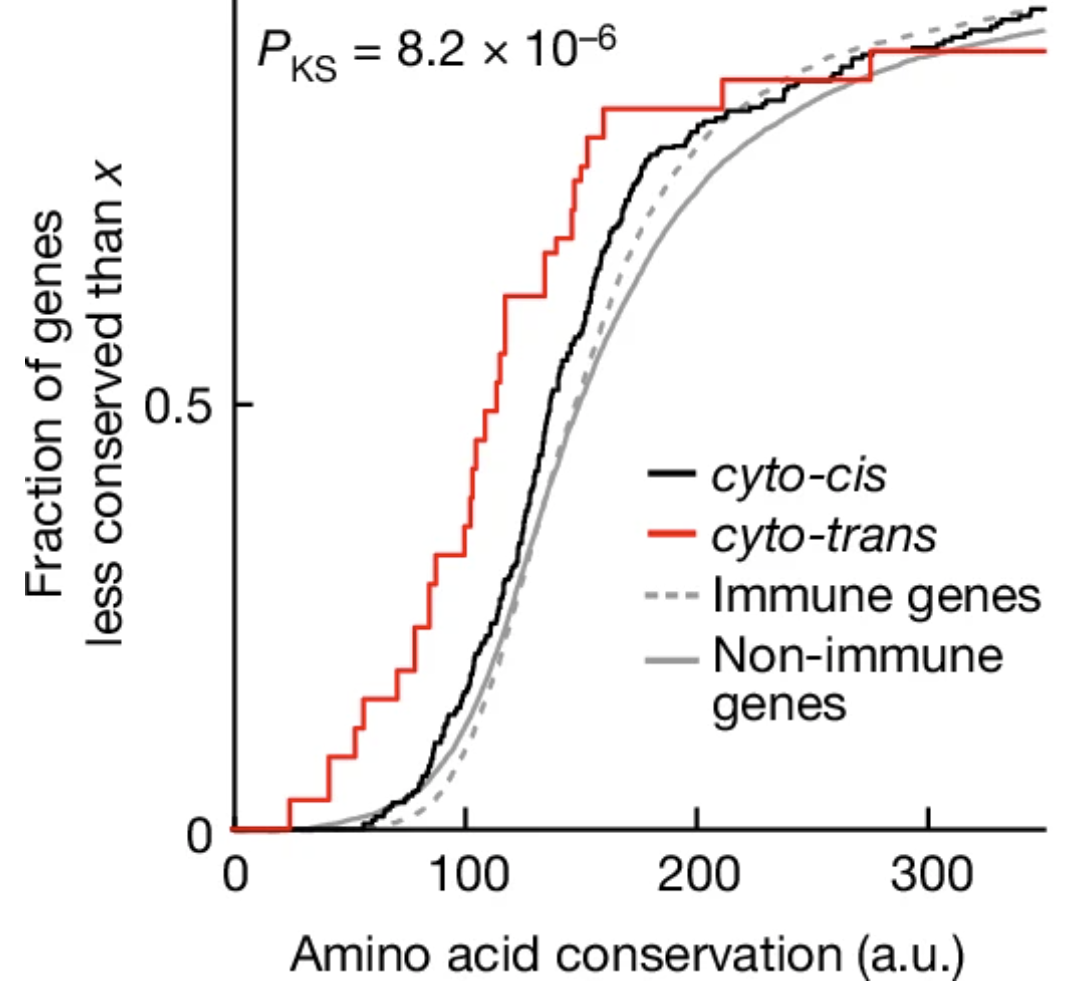
Why is there so many subtypes of immune cells? In this work, we look at what allows the immune system to evolve quicker than other systems in mammalian organisms and we find that it is the modular organisation of the immune system into many interacting cell types that allows a quick evolution of the genes involved in the interaction while preserving the core function of each cell type.
Dubovik*, T., Lukačišin*, M., Starosvetsky, E., LeRoy, B., Normand, R., Admon, Y., Alpert, A., Ofran, Y., G'Sell, M. & Shen-Orr, S.S.
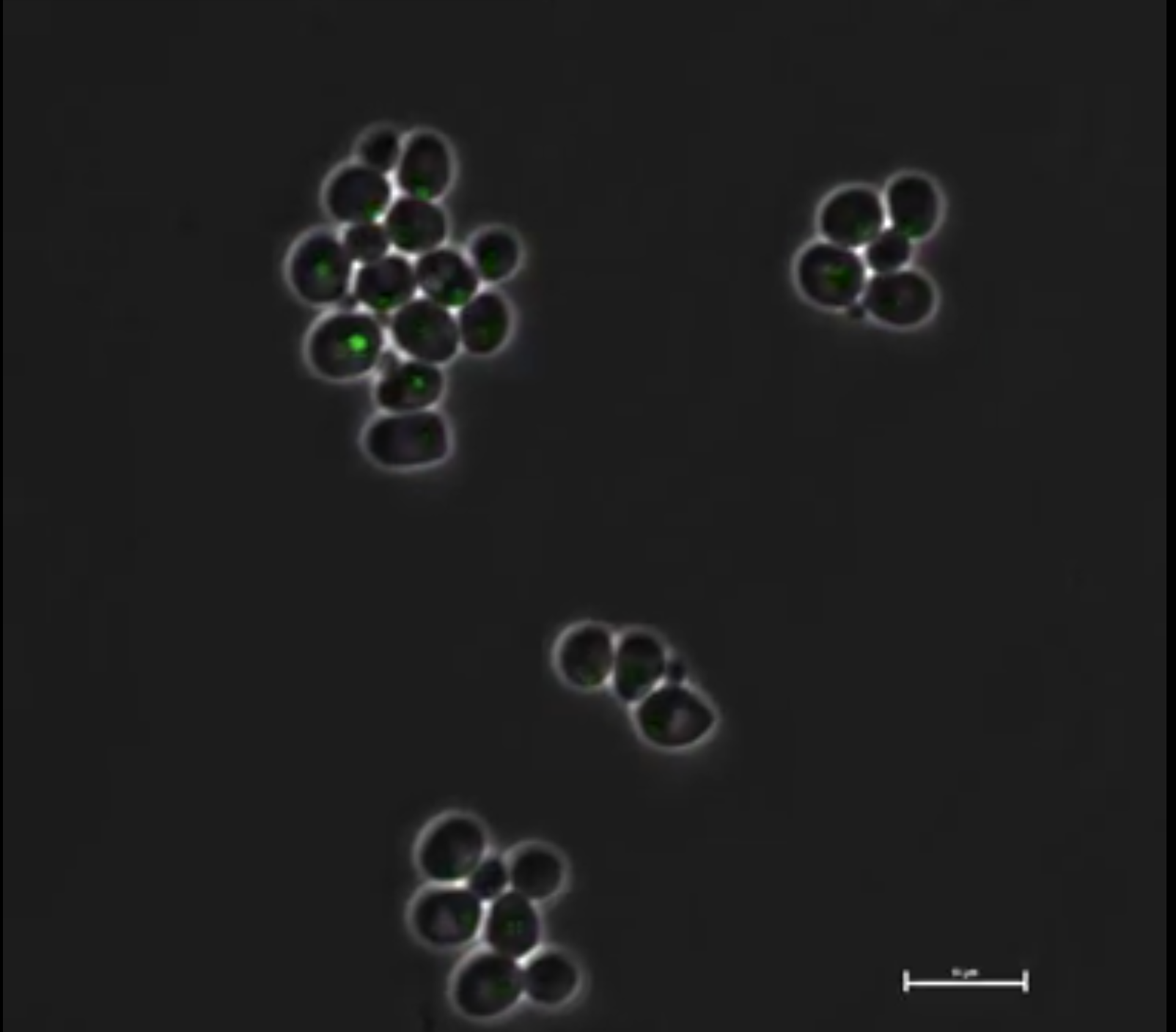
What is the function of abundant introns, otherwise very rare in the budding yeast, in the ribosomal protein genes? Using isogrowth profiling to carefully control for growth rate while perturbing the cells with osmotic stress we discover a new function for introns - diversification of the isogenic population into two subgroups, each of those better equipped to different scenarios regarding nutrient abundance.
Lukačišin*, M., Espinosa-Cantú*, A., Bollenbach, T.
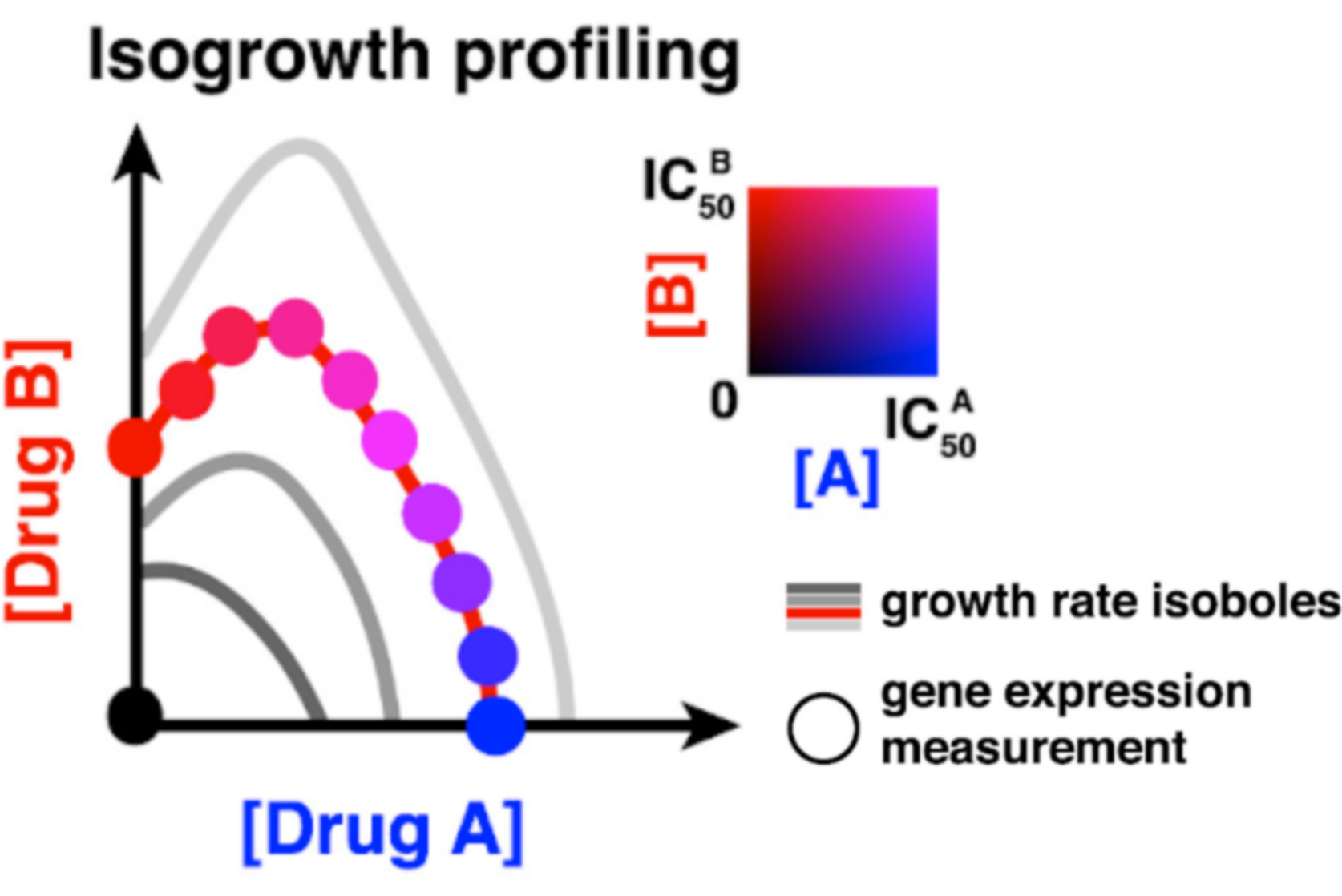
Gene expression changes due to inhibition by small molecule inhibitors should in principle give us clues about mechanism-of-action of the drug and also allow us to predict its interaction with other drugs. However, the measurement of drug-specific effect are far too often confounded by gene expression changes due to altered growth rate. Here we develop isogrowth profiling, a method where we titre out the growth inhibition precisely using various ratios of two diffent inhibitors. This allowed us to disentangle the growht inhibition-dependent, drug-specific and drug combination-specific gene expression changes and predict higher-order drug antagonisms.
Lukačišin, M., Bollenbach, T.
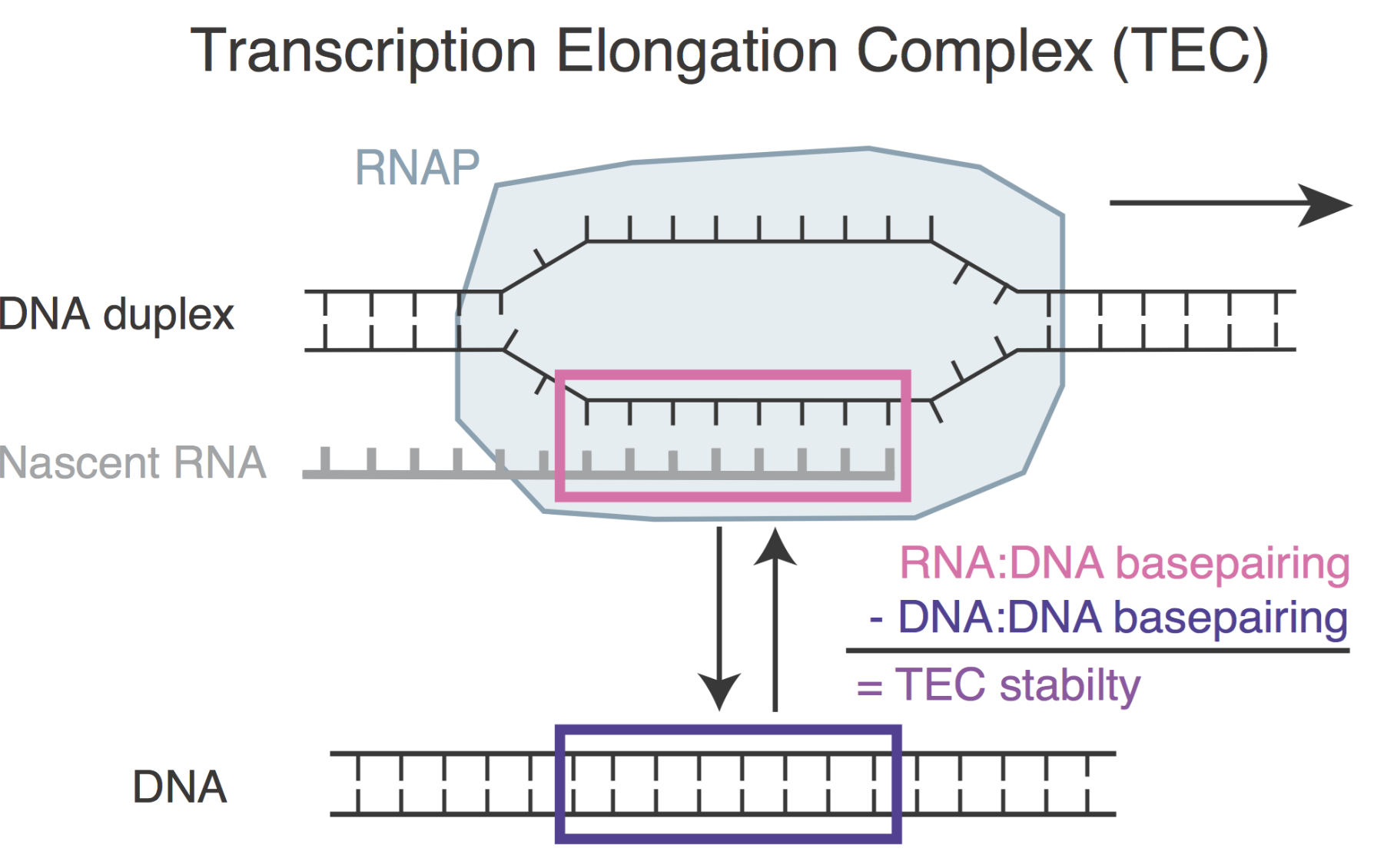
What makes RNA polymerase II pause during transcription? In eukaryotes, the prevailing opinion has been that it is the incompletely removed nucleosomes. In this work, we show that basepairing energies in front and behind the transcription bubble are sufficient to explain the pausing observed using genome-wide methods and do so much better than known nucleosomes positions. By deriving emprical relationship between basepairing energy difference and pausing propensity, we further go on to show that decreased basepairing of mismatched RNA:DNA is sufficient for triggering error correction by backtracking, widely believed to be dependent on kinetic discrimination.
Lukačišin*, M., Landon*, M., Jajoo*, R.
PLoS ONE 12(3): e0174066 (2017)

Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is a fundamental process in both development and cancer progression. In this work we show that the transcription factor Elf5 acts not only in breast tissue development, but is also an upstream regulator of the key EMT inducer Snail2. This makes Elf5 the upstream-most known regulator of cell morphology changes required for tumour cell invasiveness and metastasis.
Chakrabarti, R., Hwang, J., Blanco, M.A., Wei, Y., Lukačišin, M., Romano, R.A., Smalley, K., Liu, S., Yang, Q., Ibrahim, T., Mercatali, L., Amadori, D., Haffty, B.G., Sinha, S. and Kang, Y.
Nature Cell Biology 14, 1212–1222 (2012)
Editorial by Mathsyaraja, H. and Ostrowski, M.C. Nat Cell Biol, 14:1122-3 (2012).

By mapping the repertoire of IgM-memory B cells in patients with anti-myelin associated glycoprotein neuropathy, we showed that B cell depletion by rituximab (anti-CD19) helps the responders by reducing clonal expansions of autoreactive B cells.
Maurer, M.A., Rakocevic, G., Leung, C.S., Quast, I., Lukačišin, M., Goebels, N., Münz, C., Wardemann, H., Dalakas, M. and Lünemann, J.D.
Journal of Clinical Investigation 122:1393-402 (2012)
Full List of publications
Interactions between immune cell types facilitate the evolution of immune traits
Dubovik*, T., Lukačišin*, M., Starosvetsky, E., LeRoy, B., Normand, R., Admon, Y., Alpert, A., Ofran, Y., G'Sell, M. & Shen-Orr, S.S.
Nature 632:350–356 (2024)
Single‐cell isogrowth profiling: Uniform inhibition uncovers non‐uniform drug responses
Lukačišin, M., Espinosa-Cantú, A., Bollenbach, T.
Clinical and Translational Medicine 12(8):e1005 (2022)
Intron-mediated induction of phenotypic heterogeneity
Lukačišin*, M., Espinosa-Cantú*, A., Bollenbach, T.
Nature 605:113–118 (2022)
Emergent gene expression responses to drug combinations predict higher-order drug interactions
Lukačišin, M., Bollenbach, T.
Cell Systems 9:423-433 (2019)
Sequence-specific thermodynamic properties of nucleic acids influence both transcriptional pausing and backtracking in yeast
Lukačišin*, M., Landon*, M., Jajoo*, R.
PLoS ONE 12(3): e0174066 (2017)
Elf5 inhibits the epithelial–mesenchymal transition in mammary gland development and breast cancer metastasis by transcriptionally repressing Snail2
Chakrabarti, R., Hwang, J., Blanco, M.A., Wei, Y., Lukačišin, M., Romano, R.A., Smalley, K., Liu, S., Yang, Q., Ibrahim, T., Mercatali, L., Amadori, D., Haffty, B.G., Sinha, S. and Kang, Y.
Nature Cell Biology 14, 1212–1222 (2012)
Rituximab induces sustained reduction of pathogenic memory B cell expansions during peripheral nervous system autoimmunity
Maurer, M.A., Rakocevic, G., Leung, C.S., Quast, I., Lukačišin, M., Goebels, N., Münz, C., Wardemann, H., Dalakas, M. and Lünemann, J.D.
Journal of Clinical Investigation 122:1393-402 (2012)